中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (2): 267-273.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0017
• 材料生物相容性 material biocompatibility • 上一篇 下一篇
弱激光对植入式葡萄糖传感器外膜材料壳聚糖和Nafion生物相容性的影响
沈 浩1,刘 俊2,敬微微3,索永宽1,常世杰1,沙宪政1
- 1中国医科大学公共基础学院生物医学工程教研室,辽宁省沈阳市 110012; 2厦门大学附属第一医院,福建省厦门市 361000;3中国医科大学附属第一医院,辽宁省沈阳市 110012
Weak laser effects on the biocompatibility of chitosan and Nafion as implantable glucose sensor outer materials
Shen Hao1, Liu Jun2, Jing Wei-wei3, Suo Yong-kuan1, Chang Shi-jie1, Sha Xian-zheng1
- 1Department of Biomedical Engineering, School of Fundamental Sciences, China Medical University, Shenyang 110012, Liaoning Province, China; 2The First Affiliated Hospital of Xiamen University, Xiamen 361000, Fujian Province, China; 3The First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110012, Liaoning Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
低剂量弱激光:弱激光是功率小于10 mW/cm2的激光,因为光在时间上有累加效应,激光的照射能量基于下面的公式:照射时间(s)=照射能量(J/cm2)/激光功率(W/cm2),实验中使用的照射时间和照射能量对应关系为照射2 min(照射能量为1.2 J/cm2),照射4 min(照射能量为2.4 J/cm2),照射6 min(照射能量为3.6 J/cm2)。
Nafion:是全氟化磺酸酯构成的阳离子交换剂,磺酸基对阳离子具有良好的选择性,而且机械性能良好,不溶于水,是一种不可降解的生物材料。Nafion还对一些反应能起到催化作用,由于其选择性透过的特性,所以抗干扰能力较强。
背景:通过施加外在因素可改变壳聚糖和Nafion的生物相容性。
目的:探究不同弱激光(红光、蓝光、绿光)照射对多孔壳聚糖膜和Nafion膜材料生物相容性的影响。
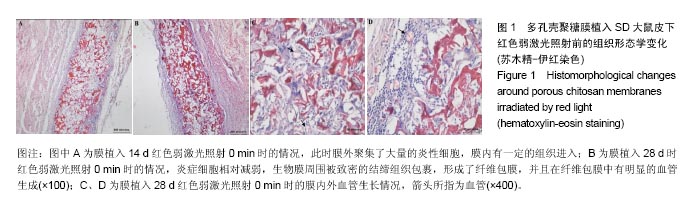
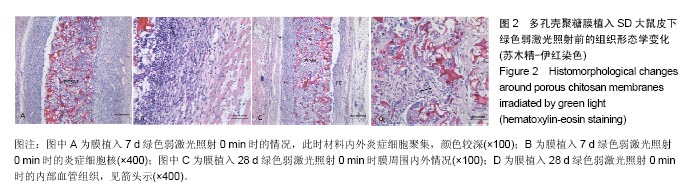
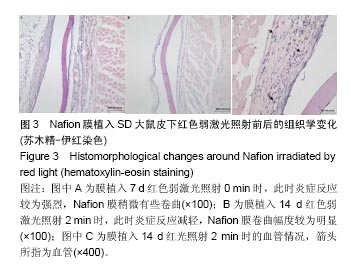
方法:①多孔壳聚糖膜实验:将48只SD大鼠随机分为红光、蓝光、绿光照射组,每组16只。沿脊柱为对称轴,在大鼠背部皮下组织两侧各植入2个多孔壳聚糖圆形膜,红光照射组每只大鼠4个膜材料分别以红色弱激光照射0,2,4,6 min,每天均在同一时间段内照射,持续照射至材料植入7,14,28,56 d取材,进行组织学分析;蓝、绿光照射处理方式同红光照射组;②Nafion膜实验:将24只SD大鼠随机分为红光、蓝光、绿光照射组,每组8只。沿脊柱为对称轴,在大鼠背部皮下组织两侧各植入2个Nafion圆形膜,红光照射组每只大鼠4个膜材料分别以红色弱激光照射0,2,4,6 min,每天均在同一时间段内照射,持续照射至材料植入7,14 d取材,进行组织学分析;蓝、绿光照射处理方式同红光照射组。
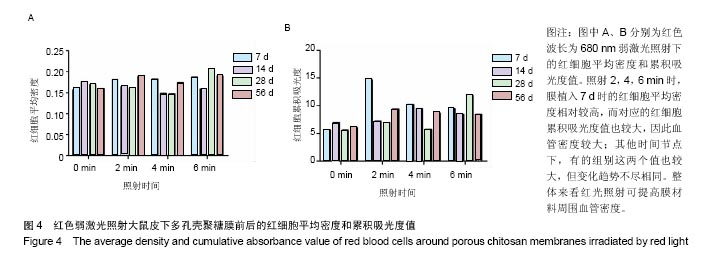
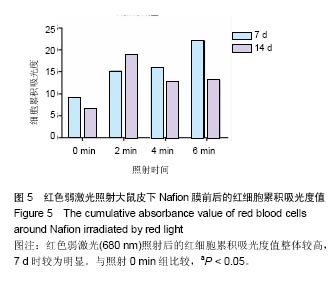
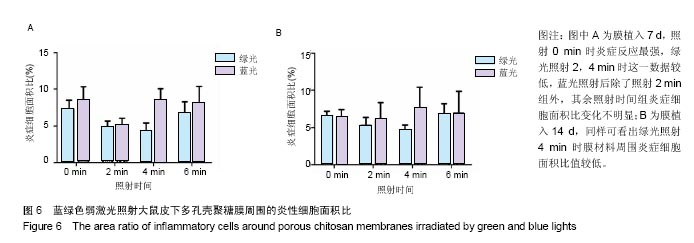
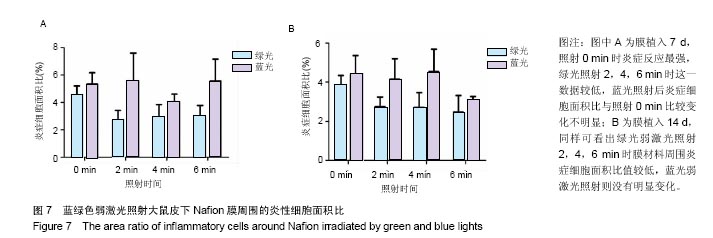
结果与结论:①红色弱激光照射后,多孔壳聚糖膜植入7 d时的红细胞平均密度相对较高,而对应的红细胞累积吸光度值也较大;其他植入时间点下,有的组别这两个值也较大,但变化趋势不尽相同,整体来看红色弱激光照射可提高膜材料周围的血管密度;②红色弱激光照射后,Nafion膜周围的血细胞密度和面积增加,植入7 d时的红细胞累积吸光度值增加较为明显,整体上,红色弱激光照射可显著提高Nafion膜周围的血管密度;③绿色弱激光照射4 min能有效减轻多孔壳聚糖膜周围炎症反应强度,而蓝色弱激光对多孔壳聚糖膜植入后的炎症影响较小;绿色弱激光可减弱Nafion膜植入7 d内的炎症反应,而蓝色弱激光没有这种效果;④红色弱激光照射对两种膜周围炎症反应和纤维包膜厚度的影响较小,蓝绿色弱激光对两种膜周围纤维包膜厚度和血管密度影响较小,而且变化无明显规律,整体上,绿光弱激光在一定程度能提高膜材料的生物相容性;⑤结果表明,弱激光照射在一定程度上能提高多孔壳聚糖膜和Nafion膜的生物相容性。
中图分类号:
.jpg)